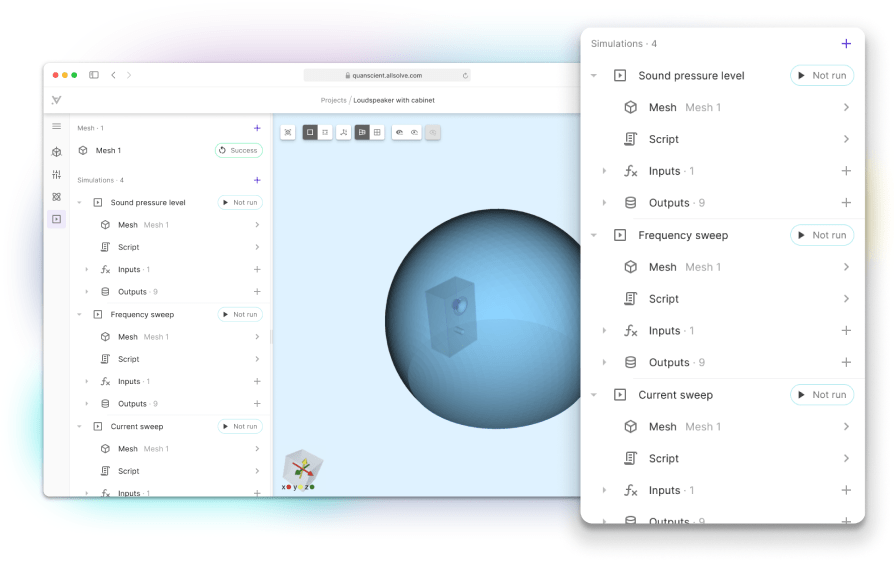
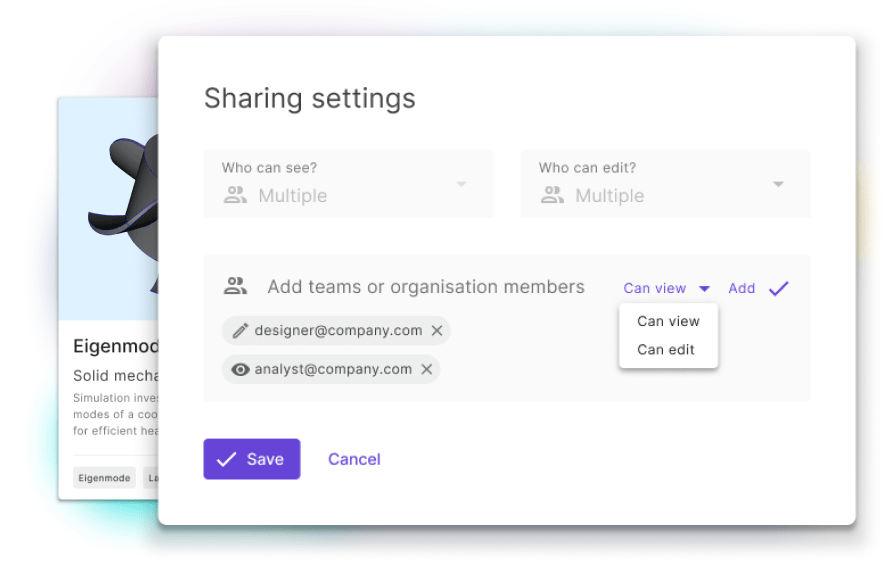
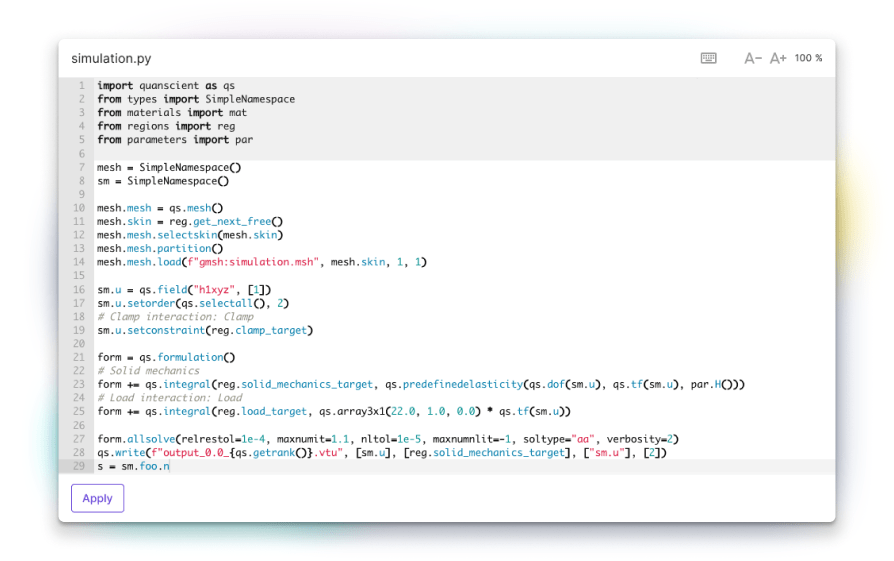
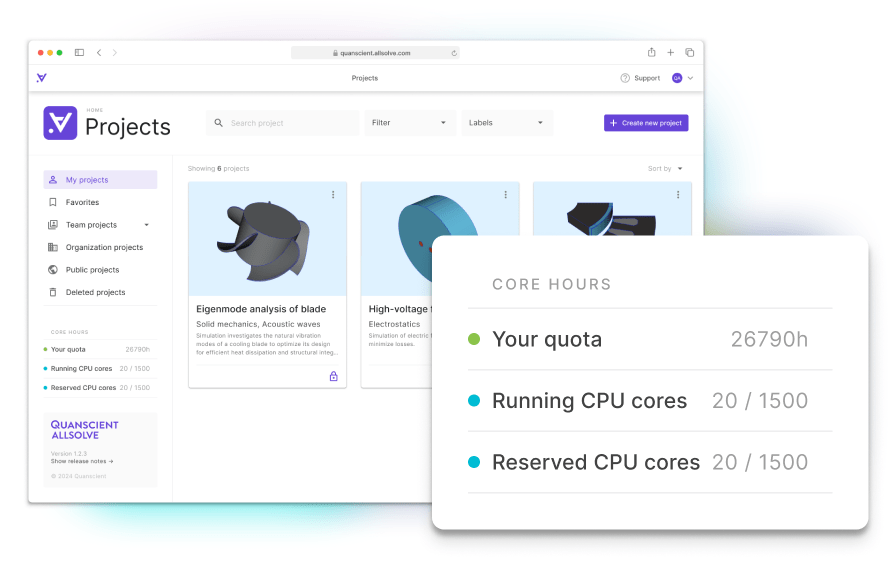
Fast, scalable, and flexible multiphysics simulation software
Get the full benefits of cloud computing with a comprehensive multiphysics simulation solution in your browser





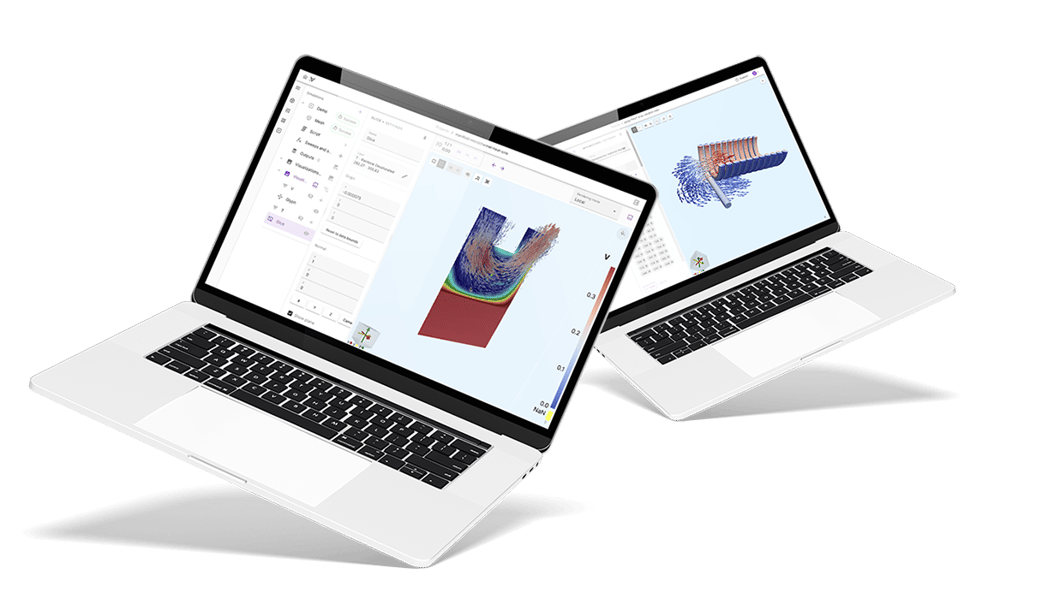
Comprehensive cloud-based simulation software for organizations of all sizes
Support and materials
Support directly from our experts one click away. Tutorial videos; user guides; documentation.
Open Quanscient Allsolve Docs
Proven applications and advantages in
MEMS
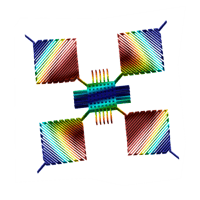
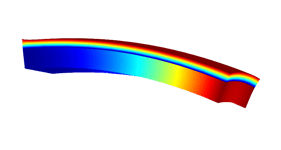
Accelerometers
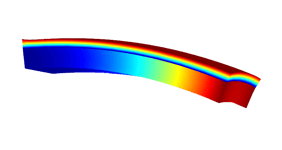
Piezoelectric devices
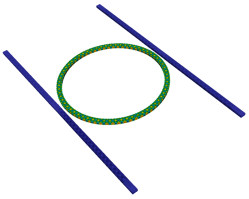
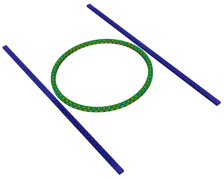
Radio Frequency (RF) components
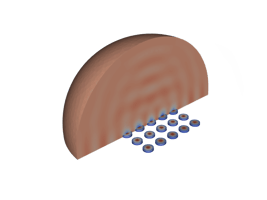
Piezoelectric Micromachined Ultrasonic Transducers (PMUTs)
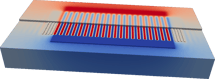
Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW) devices
MEMS
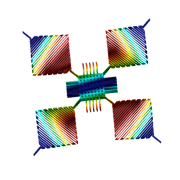
Accelerometers
Piezoelectric devices
Radio Frequency (RF) components
Piezoelectric Micromachined Ultrasonic Transducers (PMUTs)
Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW) devices
What experts say about Allsolve
![]()
"Simulation time from 3 weeks to 8 hours, with accuracy refined from 10% to 3% of experimental data."
Iana Volvach, PhD
Electromagnetic FEA Engineer, skyTran
![]()
"Quanscient Allsolve made our hardware iterations much more reliable and functional, speeding up the development process by requiring fewer hardware iterations."
Klaus Eibensteiner
Cryogenic Engineer, kiutra
![]()
"Quanscient Allsolve is a groundbreaking tool for advanced 3D superconductor simulations. They have proven to provide accurate results in a fraction of the time with their efficient scaling on cloud computing."
Antti Stenvall, PhD
Adjunct professor, Tampere University
![]()
"With Quanscient Allsolve, I am able to run complex simulations in under a day which would otherwise take a week to finish."
Nicolo Riva, PhD
PostDoc MIT at PSFC
![]()
"With Quanscient Allsolve, we found the working design in the first iteration, saving three months in product development time."
Antony Hartley
CAE Consultant, Pixieray
![]()
"Compared to other solutions, Allsolve is way easier to implement in the company and in the team as it requires no hardware and software setup. Everyone can access the same data and simulate at the same time, not requiring any local resources in the company."
Klaus Eibensteiner
Cryogenic Engineer, kiutra
The core of our cloud scaling capability
Cloud scaling through the Domain Decomposition Method (DDM)

Initialization
Geometry uploaded and prepared in the GUI
.png?width=422&height=200&name=DDM-borders%20(warped).png)
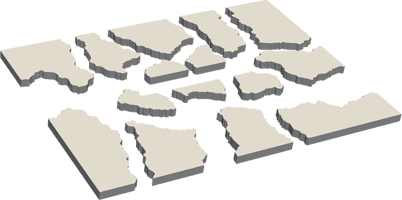
Segmenting
DDM segments your model into smaller parts for efficient processing.
Parallel processing
Distributed across multiple CPUs, each part is processed in parallel, cutting down simulation time drastically.
.png?width=422&height=200&name=DDM-visualization%20(1).png)
Integration and analysis
Once processing is complete, the results from all segments are seamlessly integrated for visualization and analysis.
The core of our cloud scaling capability
Cloud scaling through the Domain Decomposition Method (DDM)

Initialization
Geometry uploaded and prepared in the GUI
.png?width=422&height=200&name=DDM-borders%20(warped).png)
Segmenting
DDM segments your model into smaller parts for efficient processing.

Parallel processing
Distributed across multiple CPUs, each part is processed in parallel, cutting down simulation time drastically.
.png?width=422&height=200&name=DDM-visualization%20(1).png)
Integration and analysis
Once processing is complete, the results from all segments are seamlessly integrated for visualization and analysis.
Natively coupled physics and complete features for a comprehensive simulation workflow
Physics available in the GUI
Magnetism
- Magnetism A
- Magnetism H (with H-φ Coupling)
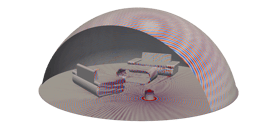
Acoustics
- Acoustics waves
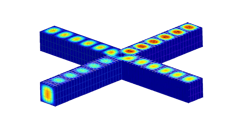
Electromagnetics
- Electromagnetic waves
- Electrostatics
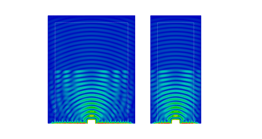
Thermal analysis
- Heat solid
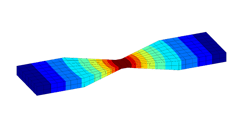
Mechanics
- Solid mechanics
- Elastic waves
- Mesh deformation
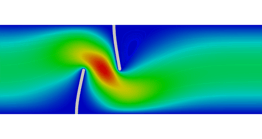
Fluid dynamics (CFD)
- Current flow
- Laminar flow
- Heat fluid
Physics available in the GUI
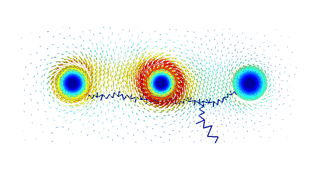
Magnetism
- Magnetism A
- Magnetism H (with H-φ Coupling)

Acoustics
- Acoustics waves
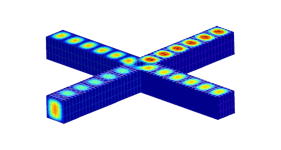
Electromagnetics
- Electromagnetic waves
- Electrostatics
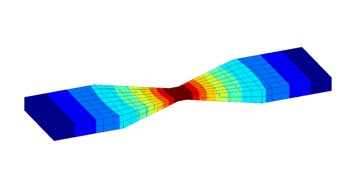
Thermal analysis
- Heat solid
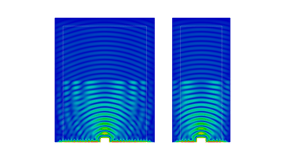
Mechanics
- Solid mechanics
- Elastic waves
- Mesh deformation
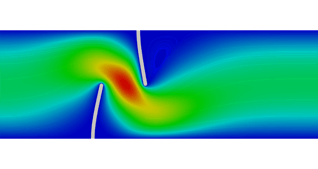
Fluid dynamics (CFD)
- Current flow
- Laminar flow
- Heat fluid
Physics available in the GUI

Magnetism
- Magnetism A
- Magnetism H (with H-φ Coupling)

Acoustics
- Acoustics waves
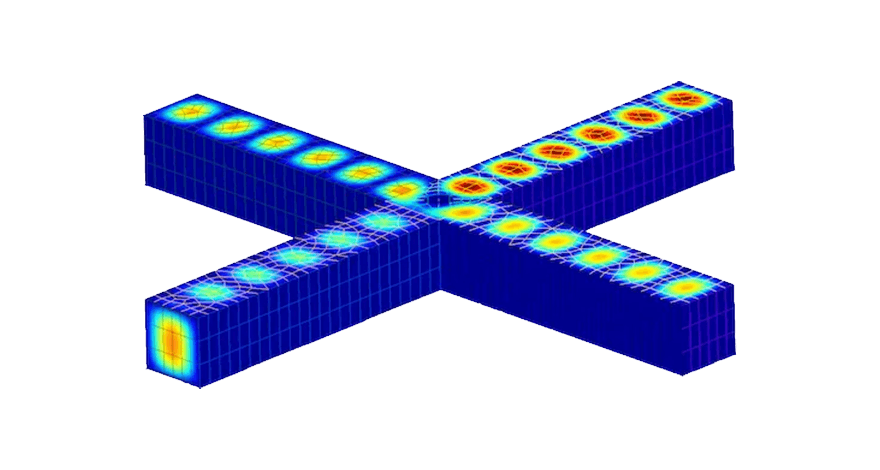
Electromagnetics
- Electromagnetic waves
- Electrostatics
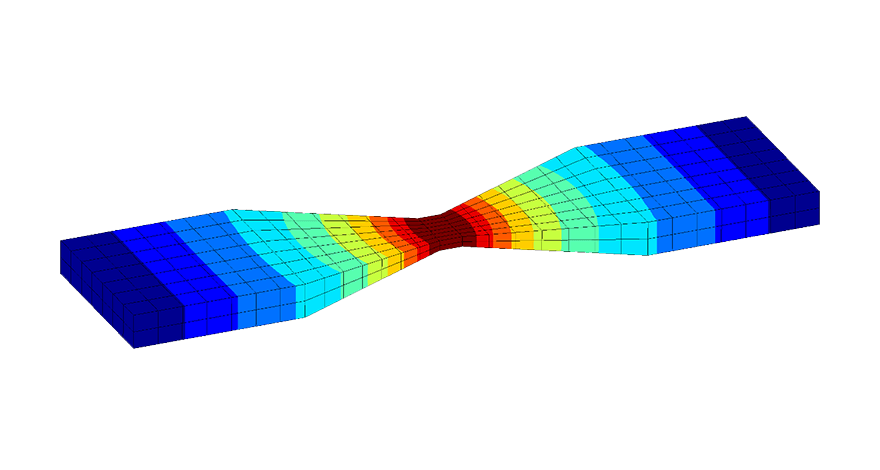
Thermal analysis
- Heat solid
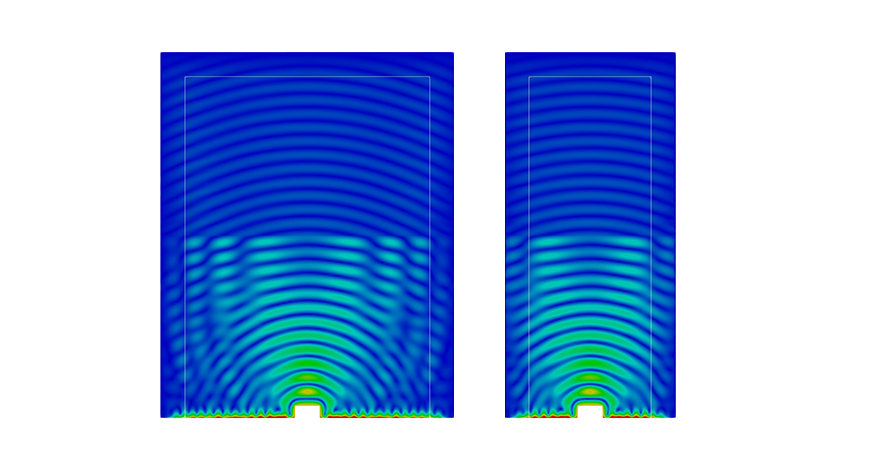
Mechanics
- Solid mechanics
- Elastic waves
- Mesh deformation
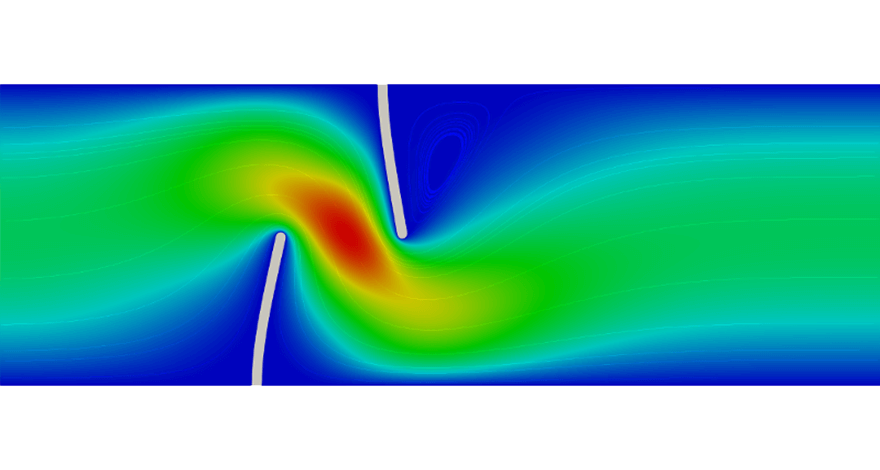
Fluid dynamics (CFD)
- Current flow
- Laminar flow
- Heat fluid
Key features and capabilities

Model import and edit
Import, edit, or create models directly within the tool.
Material management
Apply existing materials or define new ones.
Meshing options
Import or automatically generate meshes.
Comprehensive scripting
Full control via Python scripting interface for limitless customization and functionality.
Visualization and export
Conduct 3D post-processing, visualize, and export data.
Secure cloud storage
All your data and projects safely stored for access on any device.



Book an introductory call
In the 30-minute meeting, we'll:
Assess the compatibility of Quanscient Allsolve with your use case and existing workflows
Discuss pricing and evaluate the cost-effectiveness for your use case
Discover how Quanscient Allsolve could enhance your current simulation workflow and open up new possibilities
Not ready for a call yet? Let us validate your use case →
![]()
"Simulation time from 3 weeks to 8 hours, with accuracy refined from 10% to 3% of experimental data."
Iana Volvach, PhD
Electromagnetic FEA Engineer, skyTran
![]()
"Quanscient Allsolve is a groundbreaking tool for advanced 3D superconductor simulations."
Antti Stenvall, PhD
Adjunct professor, Tampere University
![]()
"With Quanscient Allsolve, I am able to run complex simulations in under a day which would otherwise take a week to finish."
Nicolo Riva, PhD
PostDoc MIT at PSFC
![]()
"With Quanscient Allsolve, we found the working design in the first iteration, saving three months in product development time."
Antony Hartley
CAE Consultant, Pixieray
In the 30-minute meeting, we'll:
Assess the compatibility of Quanscient Allsolve with your use case and existing workflows
Discuss pricing and evaluate the cost-effectiveness for your use case
Discover how Quanscient Allsolve could enhance your current simulation workflow and open up new possibilities
Not ready for a call yet? Let us validate your use case →